API functions
Based on the CBEngine, we provide APIs that share the similar parameters as the OpenAI Gym environment.
Simulation Initialization
env_config = {
"simulator_cfg_file": simulator_cfg_file,
"thread_num": 8,
"gym_dict": gym_configs,
"metric_period": 200,
"vehicle_info_path": "/starter-kit/log/"
}
env = CBEngine_rllib_class(env_config)
- simulator_cfg_file:
the path of simulator.cfg
be used for initialize engine
Example
#configuration for simulator # Time Parameters start_time_epoch = 0 max_time_epoch = 3600 # Roadnet file and flow file used to simulate road_file_addr : /starter-kit/data/roadnet_round3.txt vehicle_file_addr : /starter-kit/data/flow_round3_flow0.txt # Log configuration # Don't change the value of report_log_mode report_log_mode : normal # Log path report_log_addr : ./log/ # Log interval report_log_rate = 10 # Log configuration to track the vehicle. Don't change the value warning_stop_time_log = 100
- thread_num:
the thread number used for engine
- gym_dict:
the configuration used for initialize gym
a dict
The meaning of it is clarified at next section.
stored in /agent/gym_cfg.py, as a member variable of class
gym_cfg.
Example of
gym_dictgym_dict = { 'observation_features':['lane_vehicle_num'], 'observation_dimension':24, 'custom_observation' : False }
- metric_period:
the interval of scoring
At each intervals, output a score json file
- vehicle_info_path:
the path of vehicle informaton log
Environment Configuration: gym_cfg.py
gym_cfg.py in agent folder defines the configuration of gym environment. Currently it contains observation features. There are two options in observation features, namely lane_speed , lane_vehicle_num, which determines the content of observations you get from the env.step() api. You must write at least one of the two features.
class gym_cfg():
def __init__(self):
self.cfg = {
'observation_features':['lane_vehicle_num'],
'observation_dimension':24,
'custom_observation' : False
}
- self.cfg:
store the configuration of gym
custom_observation’: If ‘True’, use costom observation feature in CBEngine_round3.py. If ‘False’, use ‘observation_features’observation_features’ : Same as round2. Add ‘classic’ observation feature, which has dimension of 16. It’s order will be same as the order of observation fromenv.step()observation_dimension’ : The dimension of observation. Need to be correct both custom observation and default observation.
Simulation Step
step(actions):Simulate 10 seconds in engine.
The format of action is specified below.
return observation, reward, info, dones
The format of observations, rewards, infos and dones is specified below.
observation, reward, dones, info = env.step(action)
- actions:
Required to be a dict:
``{agent_id_1: phase_1, ... , agent_id_n: phase_n}``Set agent_id to some phase (The figure below demonstrates the allowed traffic movements in each phase)
The phase is required to be an integer in the range [1, 8] (note there is no 0)
The initial phases of all agents are set to 1
The phase of an agent will remain the same as the last phase if not specified in the dict actions
Attention: If an agent is switched to a different phase, there will be a 5 seconds period of ‘all red’ at this agent, which means all vehicles could not pass this intersection. If continuously switched to different phase, agent would be always ‘all red’.
In final round, agent_id will be str rather than int
- observations:
a dict
format:
{ # agent_id : {'observation' : obs} '12647332106' : {'observation': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1]} }
The key is agent_id (str) , the value is a dict. The dict only contains one key “observation”, and its value is a list catenated by the order in
'observation_features'ofgym_cfg.pyFormat of the
'lane_speed','lane_vehicle_num'and'classic'observations_values are described below:
# observation values: # 'lane_speed' sample: [-2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2] # There are 24 lanes left. The order of their roads is defined in 'signal' part of roadnet file # the order is :inroad0lane0, inroad0lane1, inroad0lane2, inroad1lane0 ... inroad3lane2, outroad0lane0, outroad0lane1 ... # Note that, [lane0, lane1, lane2] indicates the [left_turn lane, approach lane, right_turn lane] repespectively of the corresponding road. # The order of roads are determined clockwise. # If there is a -1 in the signal part of roadnet file (which indicates this road doesn't exist), then the returned observation of the corresponding lanes on this road are also 3 -1s. # -2 indicating there's no vehicle on this lane # 'lane_vehcile_num' sample [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,] # There are 24 lanes left. The order of their roads is defined in 'signal' part of roadnet file # the order is :inroad0lane0, inroad0lane1, inroad0lane2, inroad1lane0 ... inroad3lane2, outroad0lane0, outroad0lane1 ... # If there is -1 in signal part of roadnet file, then the lane of this road is filled with three -1. # 'classic' sample: [1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 2, 1, 4, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] # the first 8 values are the number of vehicles of left-turing and go-straight lanes ordered by the 'signal' part of roadnet file # the last 8 values are the one-hot code indicates which lanes are available in last signal phase
- rewards:
a dict
key is str
must implement in
CBEngine_round3{agent_id_1: reward_values_1, …, agent_id_n: reward_values_n}
Format of reward_values:
reward in rllib needs to be single values. We provide 2 types of rewards definition as demos,
pressureandqueue length, along with the old rewards.
# Sample Output { 0: -0.5 }
Here is an illustration of the lane index in observation and reward.
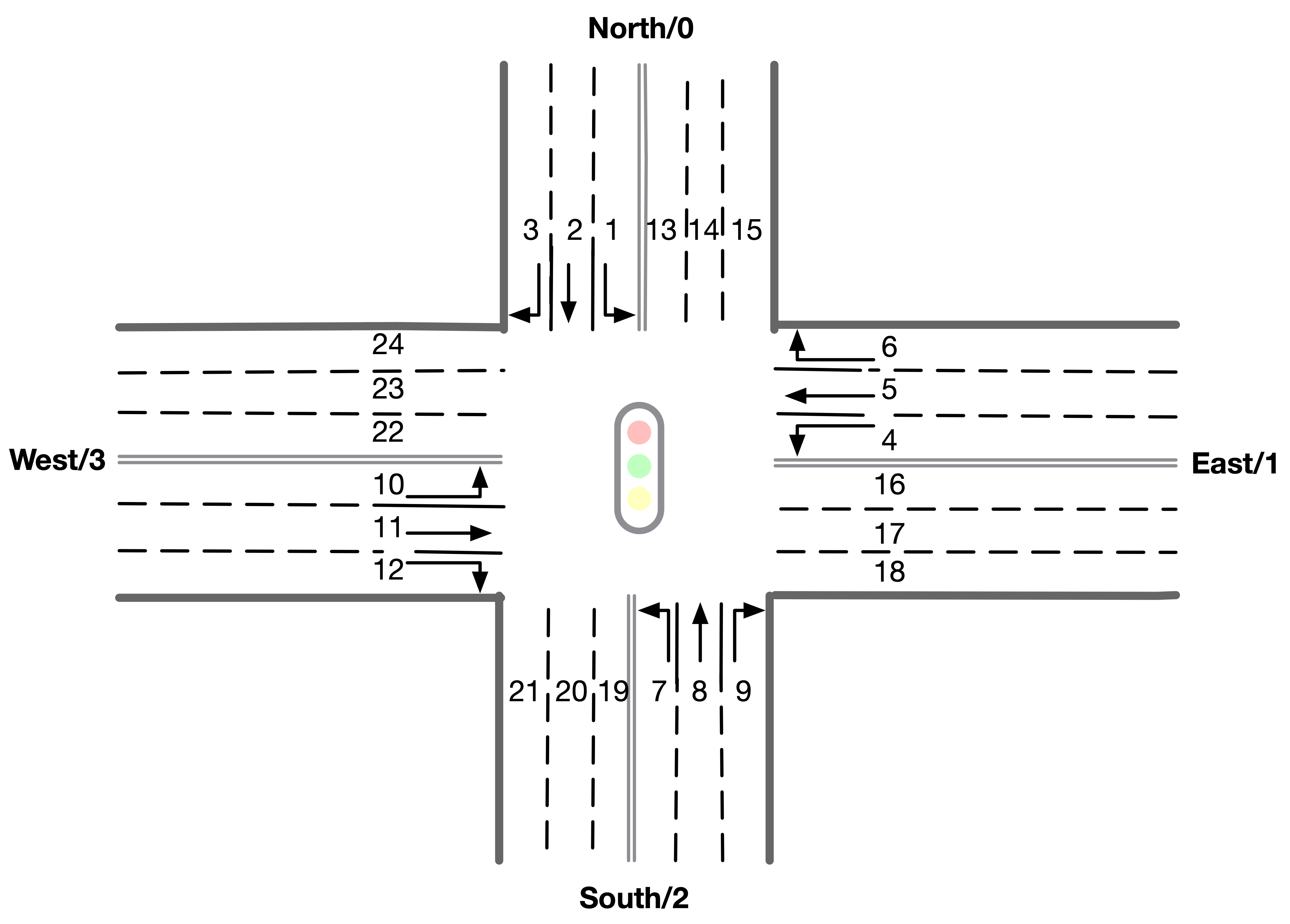
- info:
a dict
key is vehicle ID, values includes ‘distance’, ‘drivable’, ‘road’, ‘speed’ and ‘start_time’
{vehicle_id_1: vehicle_info_1, …, vehicle_id_m: vehicle_info_m}
env.set_info(1) to return a dictionary of vehicle information, otherwise, return an empty dictionary.
“route” and “t_ff” are removed from “vehicle_info” in final phase
0: # 0 is the vehicle ID { "distance": [259.0], # The distance from this vehicle to the start point of current road. "drivable": [29301.0], # Current lane of this vehicle. Here 293 is the road segment ID, 01 indicates the middle lane (00 and 02 indicate inner and outer lanes respectively) "road": [293.0], # Current road of this vehicle. "speed": [0.0], # Current instantaneous speed of this vehicle. "start_time": [73.0], # Time of creation of this vehicle. }, ... }
- dones:
a dict
{agent_id_1: bool_value_1, …, agent_id_n: bool_value_n}
Indicating whether the simulation of an agent is ended.
Simulation Reset
reset:Reset the simulation
return a dict: observation
reset the engine
observation = env.reset()
Other interface
The following interfaces of simulation environment are also provided:
set_warning(flag):env.set_warning(0): set flag as False to turn off the warning of invalid phases. The warning will be issued if a green phase to an inexistent lane.
set_log(flag):env.set_log(0): set flag as False to turn off logs for a faster speed when training. Note that the score function will not work if the logging is turned off.
set_ui(flag):env.set_ui(0): set flag as False to turn off visualization logs for a faster speed when training.
set_info(flag):env.set_info(0): set flag as False to make info that returned from env.step to be None, which can make training faster.